The WordPress administration panel is the back-end interface of a WordPress site that allows you to manage your site’s content and settings. We also know it as the “dashboard”.
WordPress “dashboard” is the control centre for your WordPress website. It is where you will add and manage your content, change your website settings, install plugins for additional functionality, control SEO and much more.
WordPress is designed to be easy to use, even for beginners. However, it can also be customized to fit the needs of more advanced users. Whether you are just starting WordPress or a seasoned veteran, the Administration Panel is essential for managing your website.
The admin panel is divided into sections, each with an options menu. The sections are Dashboard, Posts, Media, Pages, Comments, Appearance, Plugins, Users, Tools, and Settings. You may see more options in the sidebar because of installed plugins and theme features.
WordPress.com and WordPress.org are two different things – learn here
Let’s take a look at these sections, one by one –
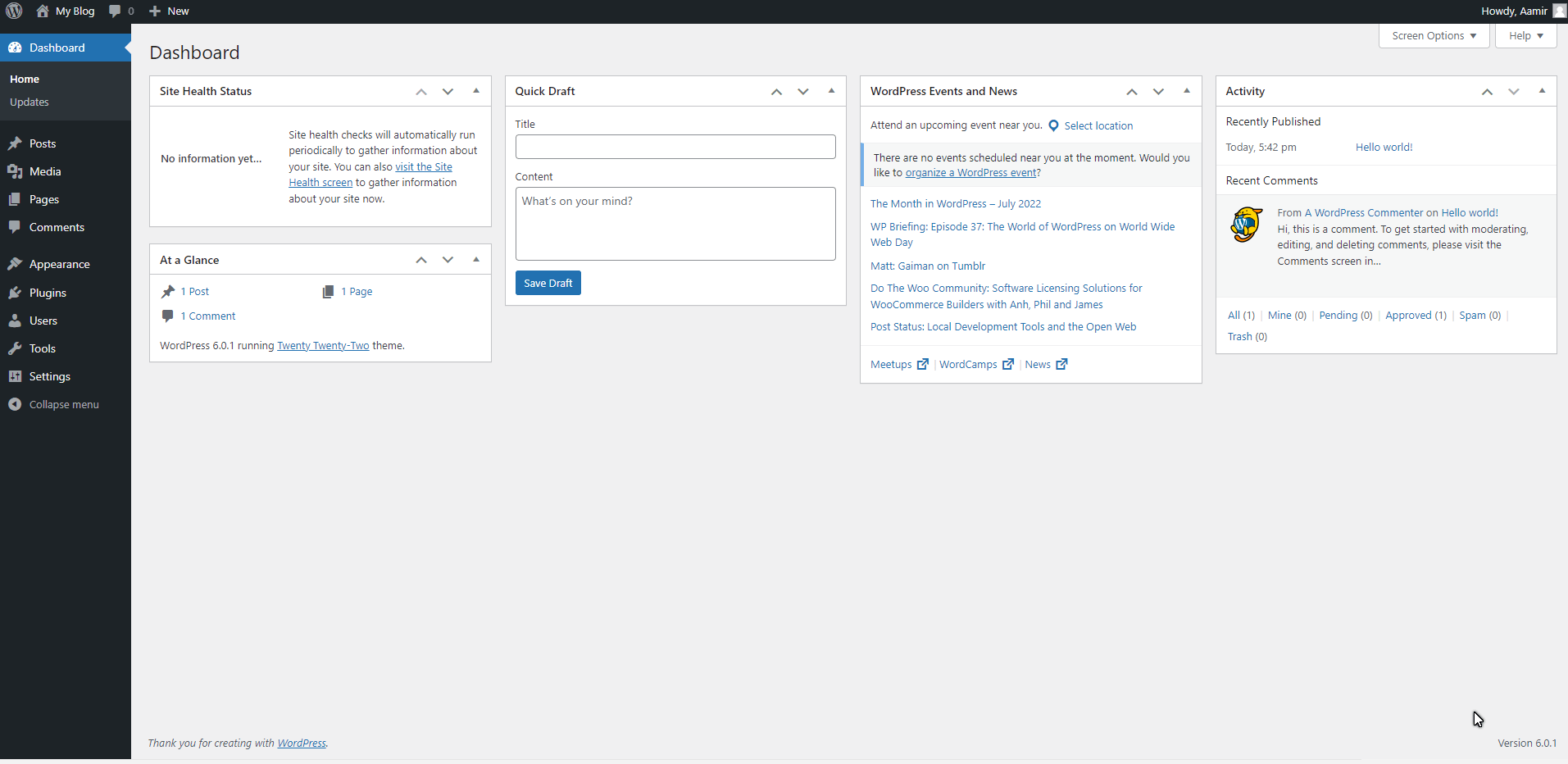
Home – The main home provides an overview of the most recent activity on the site, as well as quick links to the most commonly used admin panel features. You can also check Site health. Quickly create a draft and check out the WordPress Events & News directly from the Dashboard. You can even check site stats and how many visitors reached your website from the Dashboard, but you have to add a plugin for this feature.
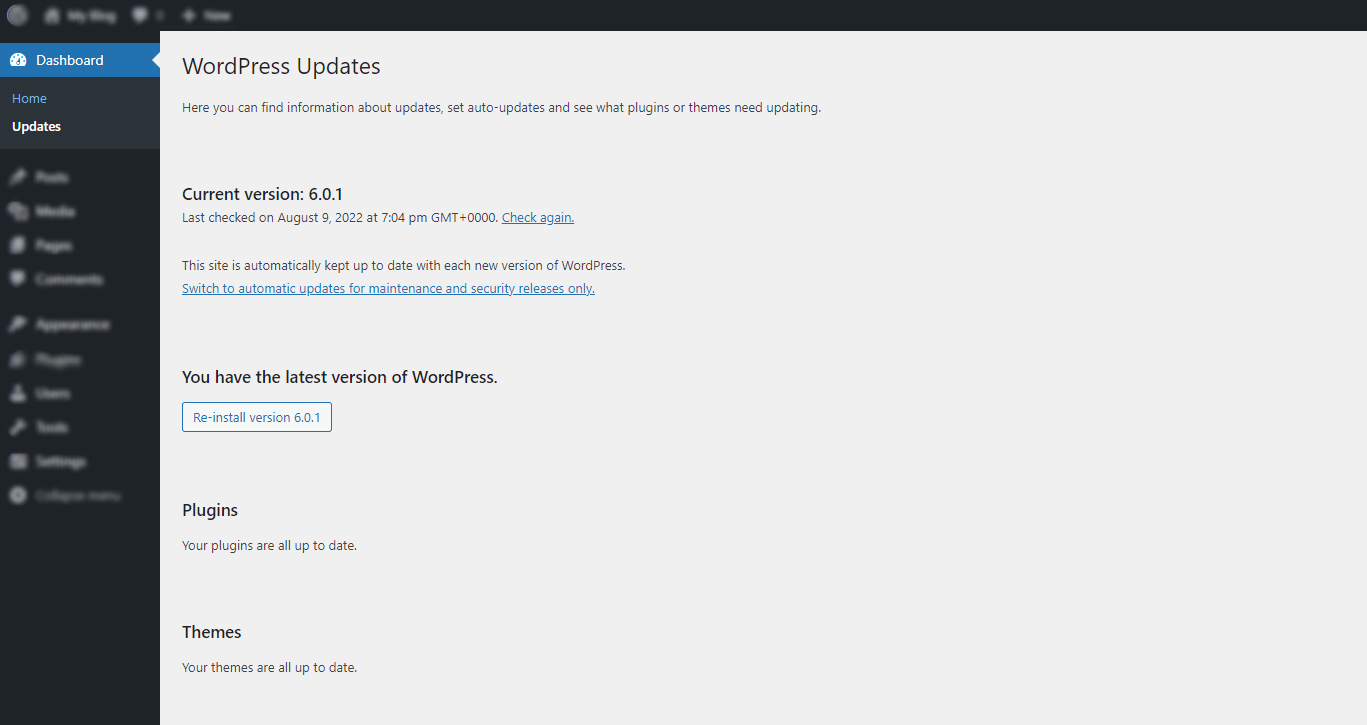
Updates – WordPress is always coming out with new updates, which can be hard to keep up with. That’s why they created the Updates tab. Whenever there’s a new update available, you’ll see it right away in the Updates tab—no more missed updates! And if you’re ever feeling curious, you can always check out the Change Log to see what’s changed in the latest update. So go ahead and update your WordPress site today.
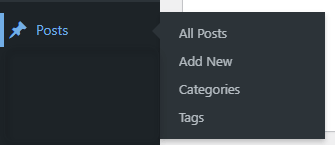
Post – This tab is where you go to create new posts, edit existing ones, and delete ones that you no longer need. But what exactly is a post? In WordPress, a post is a piece of content that can be displayed on your website. This could be a blog entry, an article, or even a short update. You can think of it like a page in a book – each post has its title and content, and you can add images and other multimedia to make it more engaging. Once you’ve created a post, it will be automatically added to your site’s RSS feed, meaning that subscribers will be able to see it when they check for new content.
If you want more control over your posts’ display, you can use the “Categories” and “Tags” tools to organize them into groups.
Categories also work as archive pages. You can set archive pages so visitors can see all the posts under their respective categories.
Media – The media tab on WordPress is a great way to manage your photos, videos, and other media files. You can also use the media tab to edit media files that have already been uploaded to your site. For example, you can crop or resize an image or change its title or description. The media tab is a great way to keep your media files organized and quickly found. All the images you directly add to your posts and pages will be shown under the media tab.
Pages – You can create new pages, edit existing ones, and view a list of all the pages on your site. The Pages tab also allows you to set up redirects, which is handy if you want to move a page to a new location. You can also use the Pages tab to create a password-protected page or restrict access to specific users. Overall, the Pages tab is a powerful tool that can help you keep your site organized and running smoothly.
Comments – The comments tab on WordPress helps keep track of all the comments made on a site. This is helpful for the site owner and visitors, as it allows everyone to see what has been said and reply if necessary. The comments tab also helps to track who has made each comment, which can be helpful if there are any disputes. In addition, the comments tab can be used to moderate comments, ensure that only appropriate content is posted, and keep spam under control.
Appearance – The appearance tab on WordPress is where you can change the look and feel of your site. There are three main sections: themes, customizations, widgets, and menus.
Themes allow you to change the overall look of your site by changing themes in just a few clicks, while customizations let you change specific aspects like the header or background. Widgets are small blocks of content that you can add to your sidebars or other site areas. The menu is for creating a direct link to the important page on your website. This improves navigation on the website and makes your website easy to navigate.
The appearance tab is a great way to personalize your WordPress site and make it look how you want it.
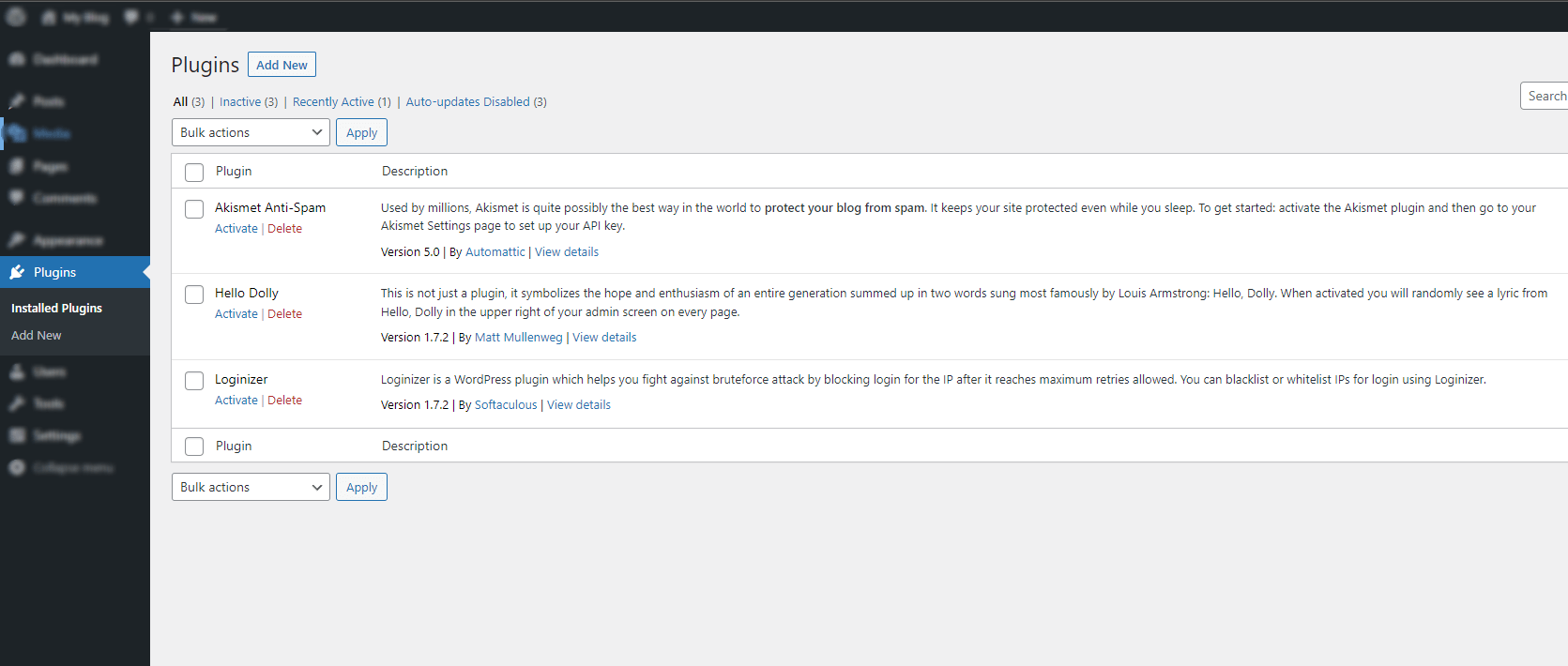
Plugins – The Plugin tab is where you manage all the plugins installed on your WordPress site. This is where you can activate or deactivate plugins and delete them if you no longer need them. You can also add new plugins from this tab by searching for them in the WordPress plugin directory or uploading them from your computer.
If you have many plugins installed, you can use the PluginFilter to sort them by name, author, or active status. The Plugin tab is a great way to keep track of all the plugins installed on your WordPress site.
Users – The Users tab in WordPress is where you can manage all your site users. This includes adding new users, editing existing users, and deleting users. You can also set the role for each user, which determines what they can and cannot do on your site.
For example, you can give a user the role of administrator, which allows them to access all the features of your site, or you can provide them with the role of editor, which will enable them to edit posts and pages but not create new ones. The Users tab is a powerful tool that allows you to control who can access your site and what they can do.
Import: The import tab in WordPress is a handy tool that lets you quickly import content from another WordPress site or a website/blog developed on another platform. This can be useful if you are migrating a site to WordPress or if you want to import a few posts or pages from another WordPress site.
To use the import tab, navigate to the Tools > Import page in your WordPress admin panel. You can select the WordPress importer tool and then follow the prompts to import your content. If you run into any problems, be sure to check the FAQ section on the WordPress codex for more help.
Export – The Export Tool in WordPress allows you to export your content as an XML file. This file can then be imported into another WordPress site. This is a helpful tool for moving your content from one site to another. The Export Tool will also save any attached files, such as images, so they can be imported into the new site. To use the Export Tool, select the content you want to export and click on the Export button. You can then download the file or save it to your computer. Once the file has been downloaded, you can import it into the new WordPress site.
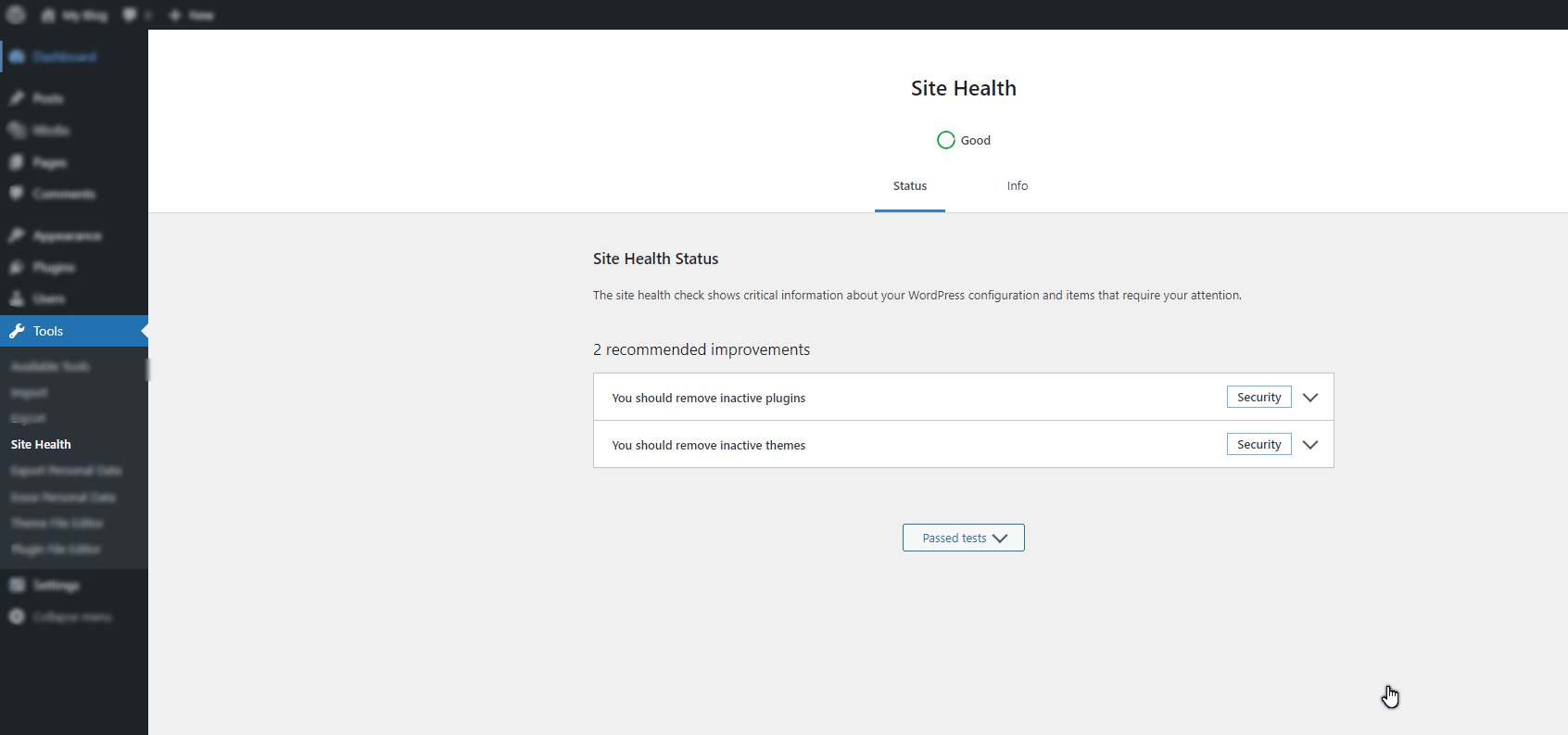
Site Health: This feature was introduced in WordPress 5.2 and is designed to help you keep your site in good working order. The Site Health tab provides an overview of your site’s performance and security and any known issues that need to be fixed. It also offers helpful tips on how to improve your site’s health. For example, the Site Health tab can help you determine if your site is running the latest WordPress version and whether all of your plugins are up to date. It can also help you identify any vulnerabilities in your code or configuration that could open your site to attack. Whether a WordPress beginner or a seasoned pro, the Site Health tab is a valuable resource for keeping your site running smoothly.
Theme and Plugin File Editor – WordPress’s theme and plugin file editor tab allows you to edit your theme and plugin files directly from within the WordPress interface. This is a great way to change your theme without using a separate text editor. The theme and plugin file editor tab includes several options that allow you to customize your theme and plugin files. For example, you can display line numbers and highlight code. You can also access the Theme File Editor Tab from the WordPress dashboard by going to Appearance > Editor.
But if you are not tech-savvy and do not understand codes, please avoid this.
General – The General tab in WordPress is where you can change your site’s title, tagline, and time zone. You’ll see a custom domain in the field under Site Address (URL) if you’re using a custom domain. The General tab also lets you choose the Language you want your site to be in. You can select a language from the drop-down menu. For most people, the default settings on the General tab will suffice. But if you ever need to change any of these settings, this is where you’ll do it.
Writing: Under this tab, you can select the default post category and set the post via the email feature. Post via email allows you to publish a post by sending an email to your wordpress website. You don’t need to login into WordPress to write your posts.
Reading: The Reading tab in WordPress is a great way to get more control over your blog content. By default, WordPress will display your most recent posts on your homepage. However, if you want to change how many posts are displayed or what order they are, you can do so from the Reading tab. You can also use this tab to create a custom home page for your blog. For example, you could create a static page that displays your latest post.
The Reading tab also allows you to control whether search engines index your site and whether or not RSS feeds are included in your site.
By checking search engine visibility, you can deindex your complete website from google searches.
Discussion: The Discussion tab in WordPress is a great way to stay connected with your readers and encourage comments on your blog posts. The discussion tab is default turned on for all new WordPress sites.
This allows anyone who visits your site to leave a comment on any of your blog posts. If you would like to moderate comments before they are published, you can change the settings so that you must approve all comments before they are visible to everyone.
You can also choose to receive an email notification whenever someone leaves a comment on your site. The Discussion tab is a great way to encourage interaction with your readers and make your blog more dynamic.
Media: This Media Tab allows you to set the image size. WordPress generates two sizes for each image you upload—thumbnails, Medium, and Large. You can set your preferred dimensions for the above three.
Permalinks – The Permalinks tab in WordPress allows you to choose from various permalink options, including the standard WordPress permalink structure or a custom structure you can create yourself. You can also decide whether to include the date in your permalinks and whether to use hyphens or underscores to separate words. By taking advantage of the Permalinks tab in WordPress, you can ensure that your website has a URL structure that is both user-friendly and search engine friendly.
Privacy – This tab provides default and pre-written privacy pages. You can set it as your default privacy policy page for your visitors.
Conclusion:
The WordPress Dashboard can be a little overwhelming for beginners. But it’s not so bad once you understand the different tabs and what they do. In this article, we’ve explained all of the tabs on the Dashboard and what each one does. We hope this information has been helpful and that you feel more comfortable using the WordPress Dashboard now. If you have any questions or need help with anything, please don’t hesitate to contact us.


